
Networks around the world are going through a massive transformation in which edge computing devices and edge infrastructure development hold a key role. This edge revolution is to leverage the potential of IoT that will be unleashed on the back of 5G roll out in the future not so far.
Groundbreaking technologies and solutions evolving in the SDN, NFV and Multi-Access Edge.
Computing verticals are laying a foundation for an agile and cost-effective network infrastructure. These technologies are designed to provide highly optimized and distributed compute and storage resources for the proper implementation of 5G services in an IoT heaven.
What is edge computing and why does it matter?
Edge computing is a method of improving data processing in cloud-based computing systems by performing it at the edge of the network, closer to the source of the data. There are several benefits to using edge computing technologies such as:
- Assisting with latency challenges.
- Bringing bandwidth-intensive content much closer to the user.
- Helping to enable future network infrastructure.
Much of the power processing that used to be performed at the core of the cloud, such as analyzing data now is possible through certain types of network infrastructure. As shown in the picture below, the edge helps with real-time data processing closer to the source or even on-premises.
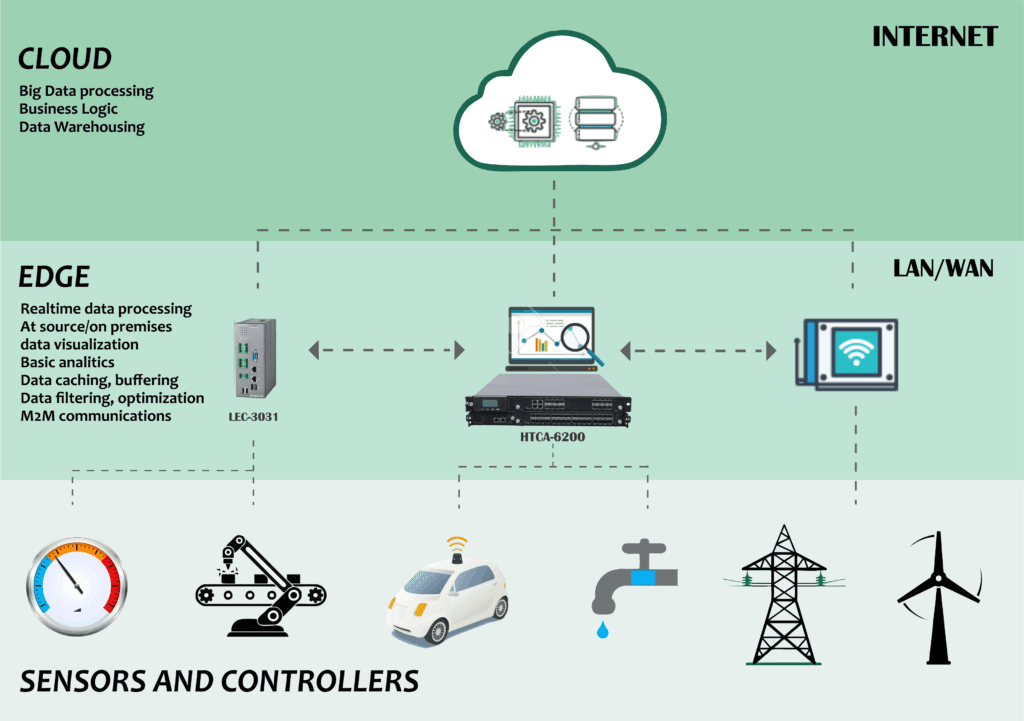
All that information from IoT sensors and controllers such as cobots, smart vehicles, smart industry, and more, does not longer need to be sent directly to the cloud. It would take a long time to send tons of data for processing to servers located across the world. These edge computing devices can analyze, buffer and cache all that data.
Within the coming years, the power of the cloud would probably be replaced by the edge.
Let’s now take a look at some of the different edge computing technologies that are being implemented now in order to help facilitate and manage the predicted increase in IoT and 5G usage.
Edge Computing Technologies
There are plenty of reasons as to why organizations might begin to employ edge computing technologies into their network infrastructure. From real-time AI data analysis and enhanced application performance, to much lower operating costs and scheduled downtime.
But what individual technologies are enabling enhanced networks such as 5G? How are they improving existing network infrastructures and what will their benefits be?
In this section, we’ll look at a few edge computing in the IoT technologies, such as mobile edge computing (MEC), fog computing, cloudlets, microdata centers, and a new concept referred to as the Cloud of Things. We’ll see what they are and how they work in order to better understand their role in enabling next-generation network infrastructures.
Multi-Access Edge Computing
Multi-access Edge Computing or Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) is a network architecture that enables the placement of computational and storage resources within the radio access network (RAN). The MEC helps to improve network efficiency and the delivery of content to end-users. In order to do this, this device can adapt to the load on the radio link to improve network efficiency and decrease the need for long-distance backhauling.
As shown in the picture below, the Fixed or Mobile Access Network which are usually located close to the end-user, in some cases one hop away, can play the role of an NFV platform.
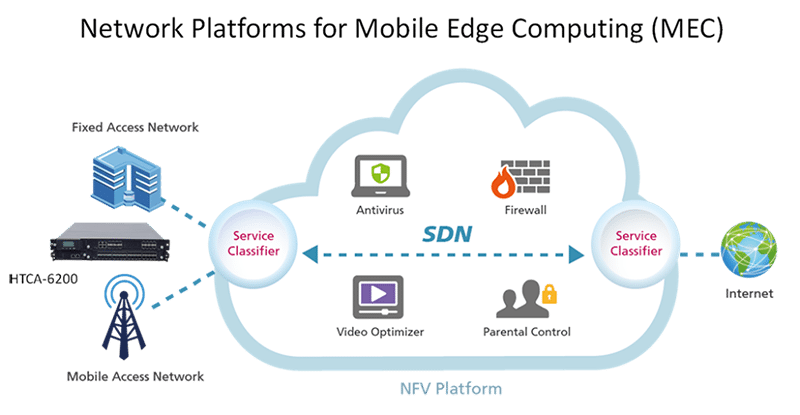
As network demands look to increase significantly as more IoT and 5G-enabled technologies and devices are developed, the mobile edge computing allows operators to deal with this excessive traffic and resource demands more intelligently. It also helps with laying the foundations for future intelligent and next-generation networks.
Mobile edge computing could also provide the enhanced location, augmented reality and Internet of Things services support. It gives those industries both a head start and time to adapt to new technologies before 5G networks begin to roll out.
Edge Computer Hardware?
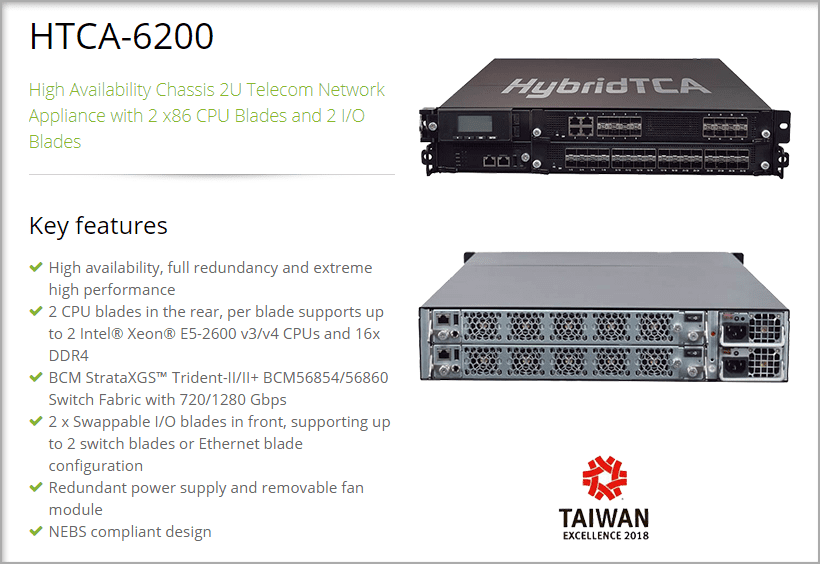
Lanner’s Edge Server HTCA-6200 is a Hybrid TCA platform with a high throughput network appliance for mission-critical edge computing applications. This appliance is great for extreme efficiency at access networks.
Fog Computing
Fog computing, fog networking or merely “fogging”, is a term used to describe a decentralized computing infrastructure. It extends cloud computing (data center) to the edge of a network while also placing data, compute, storage and applications in the most logical and efficient place. This position happens between the cloud and the origin of the data, which is sometimes known as being placed “out in the fog.”
As shown in the picture below “fog nodes” connect the edge devices with the cloud. These nodes are fog computing entities with processing and sensing capabilities.
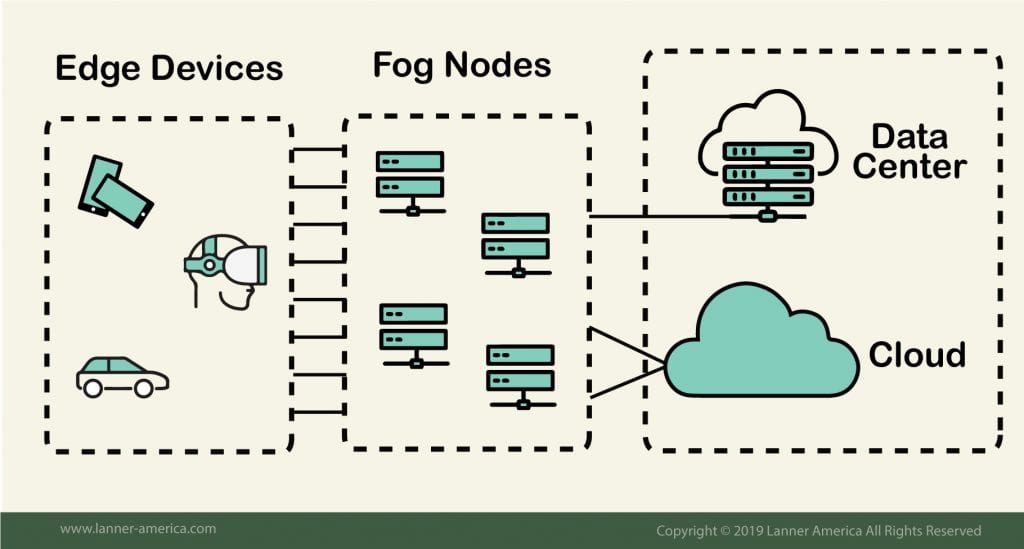
The goal behind fog computing is to both extend cloud computing and services to the edge of a network and attempt to reduce the data transported to the cloud for processing, analysis and/or storage.
The data captured from IoT sensors and other devices are usually sent to the cloud to be analyzed and processed. However, these devices can often be much too far away geographically to respond in a useful amount of time. Fog computing can enable short term analysis and processes at the edge of a network so as to reduce the amount of data being sent back to the cloud.
Cloudlets
Cloudlets are mobility-enhanced, small scale cloud data centers located at the edge of a network. They represent the second tier of the three-tier hierarchy: IoT or edge device — Cloudlet — Cloud.
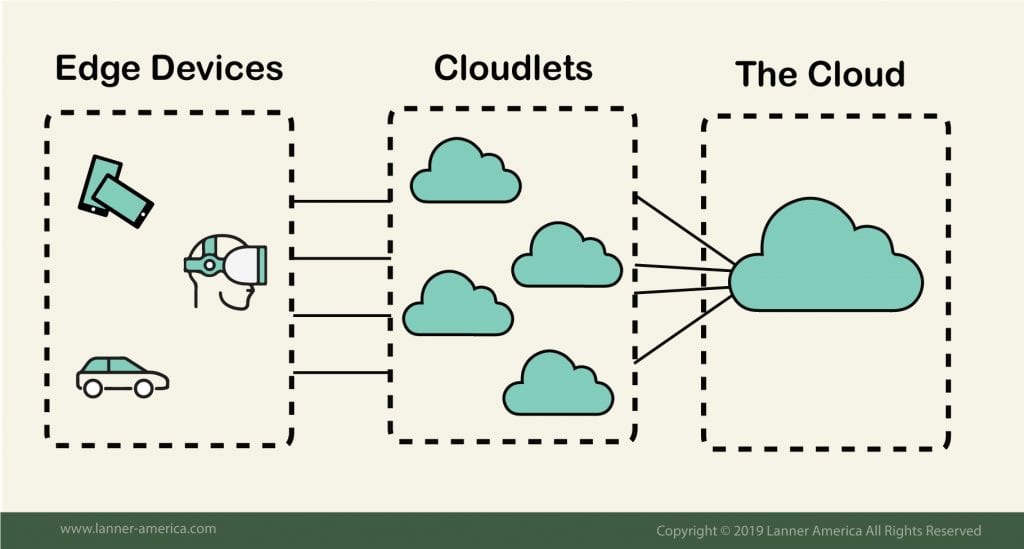
The purpose of cloudlets is to improve resource-intensive and interactive mobile applications by providing more capable computing resources with lower latency to mobile devices within close geographical proximity. This can then help to eliminate the latency delays traditionally associated with WAN cloud computing.
While 5G networks loiter on the horizon, cloudlets have been designed to support resource-intensive applications such as those for augmented reality, machine learning, speech recognition, and language processing.
Cloudlets will provide the needed assistance for 5G networks upon their arrival due to the increased demand that will come along with them. They would also need to be decentralized and widely dispersed in order to offer the greatest level of network coverage possible, this would also help with leveraging resources from nearby mobile computers.
Micro Data Centers
As the growth of the Internet of Things continues to inspire the development of new smart devices and IoT sensors, a report from MarketsandMarkets suggests that the Micro data center solution sector could be worth a staggering $32 billion over the next two and half years. It is estimated that micro data centers will be most beneficial to SMEs that don’t have their own data centers as larger corporations will tend to have more resources and thus not need such solutions.
So, what is the micro data center?
The Micro data centers are smaller, reach-level systems that provide all the essential components of a traditional data center. In certain edge computing applications, the micro data centers are much more suited than traditional data centers as they can typically be much smaller in size.
Due to the size, the micro data center can be deployed both inside and outside of rugged conditions. This makes them an ideal solution for edge computing as they can be deployed locally where the data source is and can be custom built to suit the requirements of those looking to implement them.
Cloud of Things
Cloud of Things (CoT) is still an under-developed concept, but that shows a lot of promise. In a Cloud of Things, all processing power is taken from the extreme edge, at the end-user.
We all have powerful devices in our hands, our mobiles ad IoT devices in our homes. These devices are oftentimes underutilized. Although IoT devices are still low in terms of computational power, lots of new mobiles are extremely powerful.
These devices could be orchestrated to perform a cloud service at the edge. For example, a car driving through traffic, could send warning notifications to others about traffic, and try to re-arrange other routes, without the input from the user. Using mobile devices or IoT devices could provide cloud services right at the edge.
The Cloud of Things is a similar concept as fog computing. In a CoT all IoT devices make up a virtualized cloud infrastructure. In the CoT, all the computation is performed by the IoT devices themselves which are pooled resources.
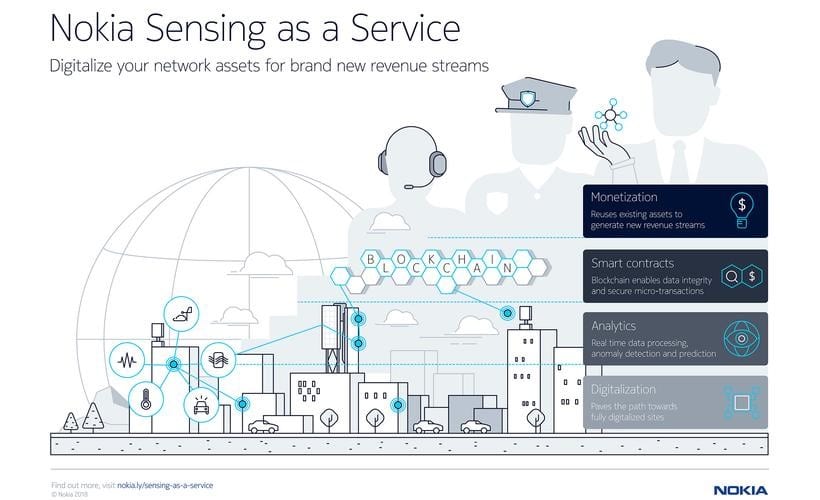
There are new CoT concepts such as Nokia’s Sensing-as-a-Service (as shown in the picture below) which uses a pool of existing edge sensing infrastructure acting as cloud agents and which are located very close to the edge. These IoT sensors can offer real-time proccing and analysis of environmental data, without needing a “Cloud”.
Final Words
We’ve now seen some of the edge computing technologies that are enabling next-generation network infrastructure. Innovations such as the continued development of the Internet of Things and 5G wireless communications networks will only remain feasible if the technologies in other areas such as mobile edge and fog computing are ready and able to provide a stable platform from which to innovate further.
MEC, fog computing, cloudlets, micro data centers, and the cloud of things will all have important roles to play when it comes to the future of network computing. Their first test, however, will be when 5G is finally ready to be rolled out.
This is an updated version of the original article published on September 24, 2017.







