With IoT sensor networks starting to develop, the Smart cities of the future are set to become reality. By blurring the lines between our physical world and cyber systems we can greatly increase our leverage of machines and computing capabilities to help facilitate and automate every aspect of our lives.
The IoT Sensors
The actual hardware that reads physical phenomenon and translates it into the 1’s and 0’s computers know and love. They can read things like temperature, pressure, motion, proximity, sounds, vibration and more. Once we equip them with low-power wireless protocols they can move onto the next step vital step for smart cities, sensor networks.
The Sensor networks


The hardware that connects all the IoT sensors to the networks is known as an IoT gateway. Combine it with an extensive deployment of IoT sensors and you’ve got an IoT sensor network. The IoT sensors connect using a special-purpose wireless connection like Zigbee or Bluetooth LE for low-power communications.
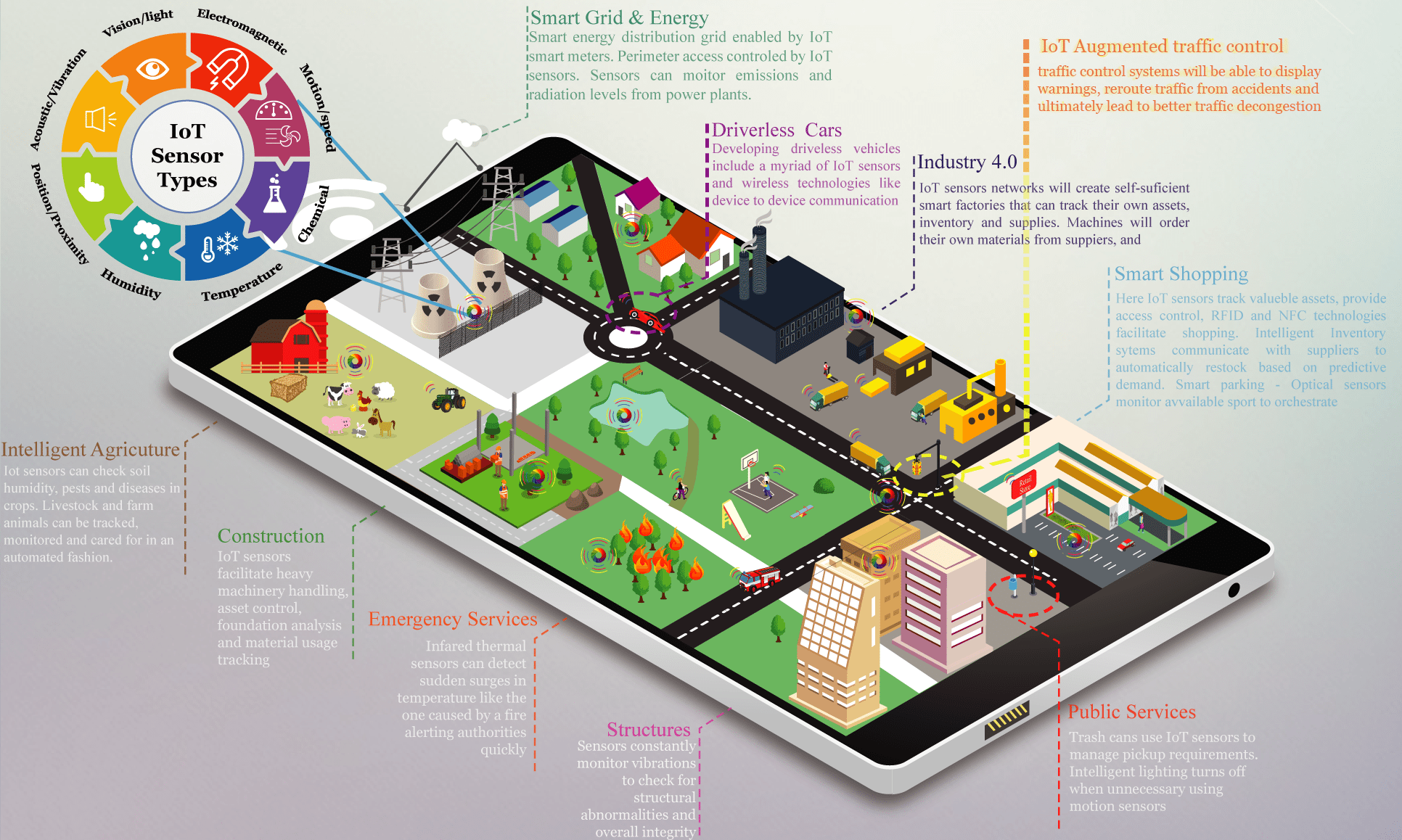
The IoT Smart City
With the sensor networks in place, many useful applications start to emerge. Below is a detailed (Hover to zoom) Infographic that show some of the most useful application put to work to form a smart city.
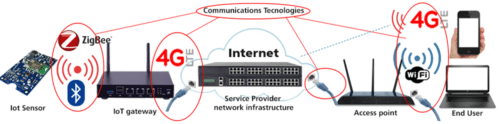
The connection broken down from user to IoT sensor
Here is an illustration of the different components in a chain between the end user and the IoT sensor. This a good example of a home automation setup(smart fire-alarm, lighting, etc). the communication goes back and forth between all these devices, utilizing communication technologies like wifi, LTE, zigbee, fiber, ethernet, etc.
Excellent Resources for further reading:
A Smart City Lighting Case Study on an OpenStack-Powered …
Renovating the Grid and Revitalizing the neighborhood case study






