
In many cases, WiFi is still the preferred method for wireless LAN deployments, and it will still be for home networks.
But when it comes to enterprise-grade networks, such as the manufacturing plant, which has a vast number of locations, connected field workers, Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) devices, and applications, WiFi has many limitations.
The lack of speed, coverage, security, and performance from WiFi networks deployed at large enterprises has opened the doors for the CBRS band and the Private LTE infrastructure.
In this article, we will highlight six main reasons why CBRS is the right ingredient for Smart Manufacturing.
The Smart Manufacturing Landscape
The birth of the Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), back in the 1970s, changed the entire history of industrial manufacturing. Most of the old manufacturing enterprises, based on the traditional mass production assembly lines, embraced PLCs and introduced industrial automation. PLCs started what we know today as the third industrial revolution.
Now we are setting foot on a new industrial revolution. We are shifting towards Industry 4.0, where automation is the de-facto standard and where new technologies are introduced.
Smart Manufacturing is built out of automation and a combination of these new technologies, including:
- Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT),
- Cloud computing,
- Edge Computing,
- and more sophisticated processes for automation, such as Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and Machine Vision.
The emergence of these technologies is painting a whole new picture on the manufacturing assembly lines. Factories can now be more efficient in their manufacturing processes.
But bridging all of these new technologies together and providing seamless transmission for the IIoT generated data, requires a new kind of connectivity.
Getting Smarter with CBRS Wireless
Manufacturing plants are now focused on improving physical Operation Technology (OT) systems and processes. A better and faster conveyor belt, a more precise robotic arm, and quicker sorting systems, which are of course critical to better manufacturing. Most of these IIoT devices, usually with wireless capabilities, generate so much valuable data, which is critical to gain business insights and improve business processes.
Unfortunately, typical wireless networks such as WiFi at the manufacturing plants do not have the speed, security, and reliability to handle such large amounts of data.
The CBRS (Citizens Broadband Radio Service) was born as a solution for these types of enterprise-grade wireless demands. It provides an unlicensed (and optional licensed) use for a portion of the 150MHz wide broadcast band of the 3.5GHz band within the United States.
Fortunately, the LTE technology can run on the CBRS-band, making the opportunity to have cellular LTE technology, as private. CBRS at band 48 is also referred to as Private LTE.
The below diagram shows a brief description of how these IIoT devices interconnect together using Private LTE CBRS technology.
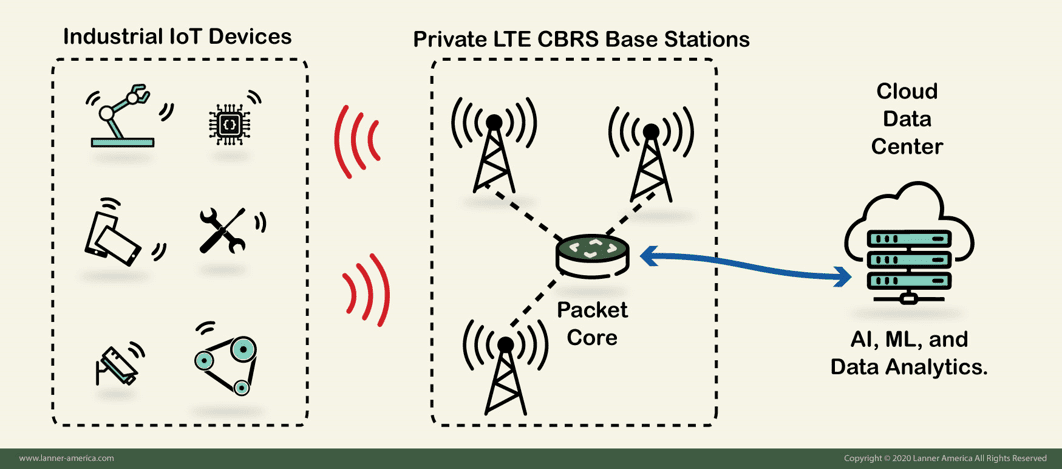
- Industrial IoT devices: Not all IIoT devices are compatible with CBRS. Most IIoT devices come with traditional interfaces like WiFi or Ethernet.
- The CBRS Gateway: IIoT may use an LTE radio module such as Lanner’s PGN-600 to provide connectivity to the CBRS network. This device acts as a CBRS Gateway to serve as a medium between CBRS devices and non-CBRS devices.
- The Private LTE CBRS Base Stations and Packet Core: These are LTE infrastructure that is compatible with CBRS. The Packet Core should have a safe connection to PDNs (Public Data Networks).
- The Cloud Data Center: Not a CBRS component, but it is key for smart manufacturing. The cloud is where complex computation happens, AI, ML, machine vision, analytics, etc.
Six Reasons Why CBRS is the right ingredient for Smart Manufacturing
As stated before, CBRS Private LTE provides the capabilities for large-scale wireless deployments.
Manufacturing plant workers and devices can be empowered with a whole suite of mobile wireless applications to improve their productivity, decision-making, and even their security. These capabilities are, of course, leveraged by the data analytics provided by edge computing servers and cloud computing.
There are six main reasons why Private LTE CBRS should be an integral component for network development in smart manufacturing.
- Dedicated Bandwidth.
- Reduced Latency.
- Wide Coverage and Mobility.
- Inherent Security.
- Scalability.
- Cost-efficiency.
Dedicated Bandwidth
The performance of a typical wireless network, such as WiFi, gets compromised when the available wireless frequencies on the spectrum are limited, and there is a large number of devices attempting to communicate.
CBRS solves this problem by providing an expanded and dedicated bandwidth to the private LTE infrastructure. The new and broad CBRS spectrum band stretches between the 3550-3700MHz. From the 150 MHz, 80-100MHz are available for the General Authorized Access (GAA) or “Private LTE”
This new bandwidth is like providing a new traffic lane for IIoT devices with wireless capabilities. These CBRS-enabled devices will not suffer from interference from the usual congested public wireless spectrum.
Reduced Latency
Some industrial automation operations require real-time responses or latencies well below 2ms. Within the plant, no WiFi technology can achieve that; only wired fiber optics would be able to return latencies as low as 2 ms.
The CBRS Private LTE is a fully independent cellular network, including the core network and cell sites. Having this type of independence allows manufacturers to optimize their networks and provide reduced latency for their specific mission-critical automation operations.
Private LTE can be configured to handle specific types of traffic with individual requirements. A certain QoS (Quality of Service) can be guaranteed for specific manufacturing processes that need extremely low latencies. Thanks to this flexibility, Private LTE can achieve latencies averaging 1-2ms.
Wide Coverage and Mobility
Manufacturers can deploy Private LTE to guarantee a wide coverage within the whole plant and even reach remote places impossible for WiFi. While WiFi devices must be located within an average of 300 feet from the wireless access point, LTE devices can connect to the base station across miles.
Private LTE provides the necessary indoor and outdoor coverage that the devices across the manufacturing floor need for reliable communication. Since Private LTE puts the whole manufacturing plant on a different frequency, the indoor devices like robots don’t have to fight for signal coverage.
But coverage is not the only advantage; Private LTE also provides seamless mobility over an entire area. The LTE technology has been designed from the ground-up to provide seamless mobile roaming.
Inherent Security
Unlike the Public LTE, which uses shared infrastructure to transmit and receive data within a range, Private LTE is built on a whole new separate private network.
The traffic between the Industrial IoT devices on the manufacturing plant and the on-premises servers remains local. Private LTE uses dedicated radio equipment and a packet core network so that all the traffic is segregated at the spectrum-level.
Another advantage of Private LTE is that the LTE endpoints use isolated SIM-based authentication and PUK codes to access the wireless infrastructure.
Scalability
Cellular technology such as Private LTE is considered to be a highly scalable and robust solution. It can quickly scale upwards and downwards. Depending on the type of traffic, a Private LTE single server can support up to 500,000 sessions with a 3-Gbps throughput.
As the demand for a manufacturing plant grows, the private LTE network can scale by adding more radio resources, without having to change the whole system.
Implementing a high-speed private LTE network allows manufacturers to gain better control of their expansion capacity. As they can choose where to grow and which resources to expand, Private LTE becomes very cost-efficient.
Cost-efficiency
WiFi network deployments in large-scale manufacturing plants are possible, but it can be quite expensive. To build a widespread WiFi network, you would need tons of WiFi equipment, repeaters, WLAN controllers, etc., which can get costly.
Private LTE provides more coverage, speed, and security, so it requires less equipment. It is a much more cost-effective solution than large-scale WiFi deployments, first because the infrastructure is less expensive, and second because manufacturers can get all the benefits listed without any additional data costs.
The manufacturer can have full autonomous control of the capacity of the network without depending on network operators or licensing costs.
Final Words
Private LTE CBRS along with other emerging technologies like AI/ML, IIoT, big data, and edge computing will move the needle and improve manufacturing production and quality, as never seen before.
Private LTE CBRS will be a key element in smart manufacturing. It will provide low latency for mission-critical applications on the manufacturing floor, avoid wireless interferences with dedicated bandwidth, provide a high level of security, extended coverage, provide high scalability, and everything at a cost-efficient price.
The LTE radio module Lanner’s PGN-600 is a good place to start. With this module, acting as a CBRS gateway, you can provide seamless communication with the non-CBRS network.






