5G is the next step in wireless telecommunications standards. Through the evolution of communications technologies and the advancement of mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets, communications networks need to be both ultra-reliable and flexible so as to adequately meet the needs of applications and data transfer requirements.
It is estimated that, by the year 2020, 12M PB of data will be transferred between connected devices and that roughly half of all connected devices will be used for business.
In order to cope with the sheer number of devices and massive volumes of accompanying data, 5G networks will have to be capable of customizing their functionality to support and deliver on the specific needs of services, devices, applications, or operators. In order to do this, next-generation wireless communications developers have recently begun to turn to network slicing as a viable technology to achieve such capabilities and further enhance 5G networks.
What Is Network Slicing?
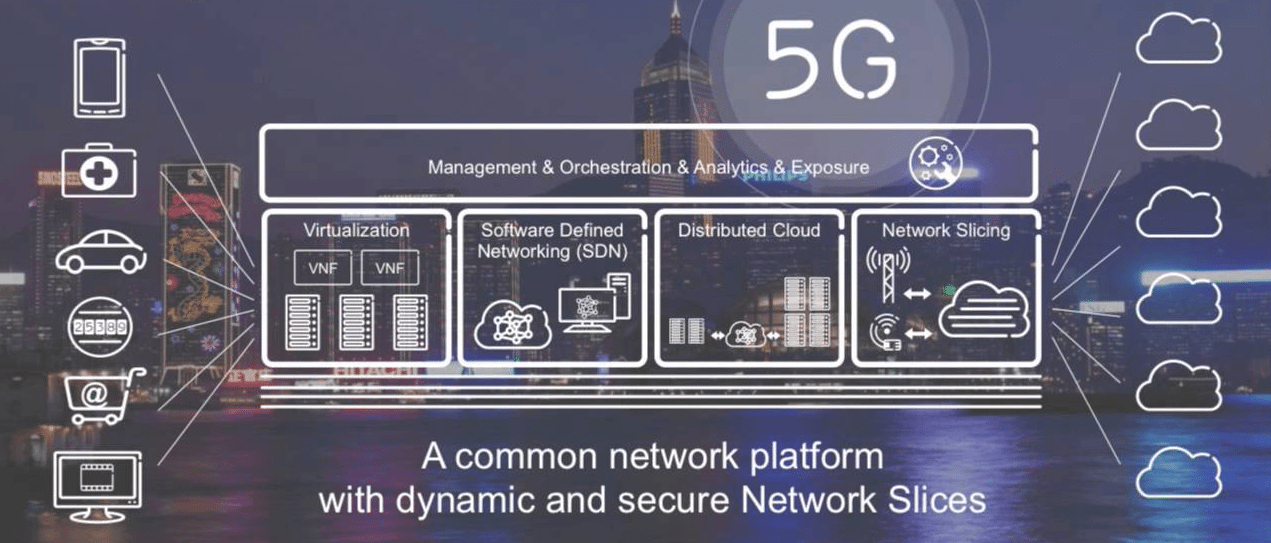
Network slicing is a network capability that allow for the creation of multiple virtual networks on top of a shared physical network infrastructure. Using similar principles to those behind software-defined networking (SDN) and network function virtualization (NFV), network slicing can introduce greater network flexibility by partitioning network architectures in virtual elements that can then be linked through software. The virtual networks that are created can then be customized to suit different network functions, applications, devices, and customer or operator needs. This will become essential in 5G networks as singular core networks can be sliced into multiple virtual networks that could each support a different radio access network (RAN) as well as the different service types running across those RANs. It is then imagined that the virtual networks would be able to cater to different requirements in a more flexible manner than previous 3G/4G networks.
Each virtual network slice would be made up of independent sets of logical network functions that were specifically customized to deal with different use cases. These slices would be isolated from one another so as to ensure that the traffic from one slice could not interfere with that of another, lowering the risk when introducing newer technologies and during migration as only individual virtual slices would be affected. As we know now, network slicing sounds like it has the potential to unlock the full potential 5G networks, but how would it do it?
Is Network Slicing The Key Technology For Enabling 5G Networks?
Now that we know how network slicing works, we can start to look at the ways in which this technology could be used to enable the full power of 5G telecommunications networks to be unleashed. In order to understand how this can be done, let’s now take a look at three of the benefits that network slicing can bring to 5G networks in order to help them reach their full potential and both enhance network functions and meet the demands of a growing number of customers and connected devices in order to deliver a powerful and reliable service.
Customized Connectivity
Network slices could also be enhanced to cater to the requirements of the specific traffic that would be using the slice. This would improve end-user experience as speed and coverage resources would be allocated based upon the demands of each individual use case. Functional components, however, could still be shared across different individual network slices so as to further increase functionality. Every slice would also have its own network provisions and engineering mechanisms as well as network provisioning to prepare and equip each virtual network slice to provide different services to its users.
Enhanced Automation
5G networks are where the Internet of Things is going to suddenly become a noticeable everyday technology. From automated cars to robotic manufacturing and smart farming IoT, 5G networks are looking to be the turning point for the Internet of Things and smart devices and IoT applications are expected to increase dramatically with the emergence and commercial availability of 5G networks. Network slicing will play a key role in enabling further IoT automation through the customization of virtual network slices. These virtual slices would be configured to specifically cater to automation-heavy industries such as transport and manufacturing so as to provide optimal virtual network conditions for automated services and operations.
Advanced SDN and NFV
In order to fully mature network slicing as an enabling technology, certain other technologies will have to evolve with it, in this case, software-defined networking (SDN) and network function virtualization (NFV). The use of open protocols to apply software control and virtualization to enable the separation of software and hardware will further enable 5G networks to provide different services to the various different kinds of users taking advantage of it. SDN, NFV, and even technologies such as machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) will all benefit from 5G networks, and so it seems completely feasible that they should all be used to enhance and enable it.
With 5G wireless communications technologies and standards loitering on the horizon, it’s easy to see why networking slicing, software-defined networking and network function virtualization have become hot topics for discussion in recent years. The evolution of wireless communications technologies has brought about many new and unforeseen use cases and applications for its related technologies and, with the Internet of Things also seemingly set on continued expansion and growth, it looks ever likely that network slicing will continue to be an essential area of both discussion and development right the way up to and even way past the eventual deployment of actual 5G wireless networks somewhere around the year 2020.
First Image Credit: Ericsson

