
Businesses rely on Internet and WAN connectivity for critical services and applications. A short-term loss on credit card processing, communications, and cloud-connected service can represent a significant loss for a business and the productivity of employees.
The high-speed and full availability of 4G/LTE Broadband Internet has made it one of the preferred choices for connectivity backup plans. An LTE Failover appliance can provide a seamless backup through the 4G/LTE mobile broadband network.
In this article, we’ll take a closer look into WAN link fails and the LTE failover appliance.
When The Primary WAN Link Fails
Distributed networks such as MSPs, ISPs, retail store chains, or enterprises need to ensure that the communication between headquarters and their branch offices is always up and running. Branch offices located at the edge network depend on continuous connectivity; they have so many important devices and applications, that they cannot risk outage.
But what happens when a primary wired WAN breaks and all data stops flowing?
When the connection between the headquarters and branch breaks, all applications, services, employee’s productivity goes to the trash.
Enterprises have had for a long time, multiple WAN MPLS links acting as active/standby or load-balancing to provide higher redundancy to their branch offices. But this approach has always been expensive and still did not offered full failover. If the pair of wires failed, the entire network at the branch failed.
Other methods used by distributed networks to provide failover to their branch offices were, using satellite as a backup link, ADSL links, and even mobile broadband such as 3G or 4G-LTE.
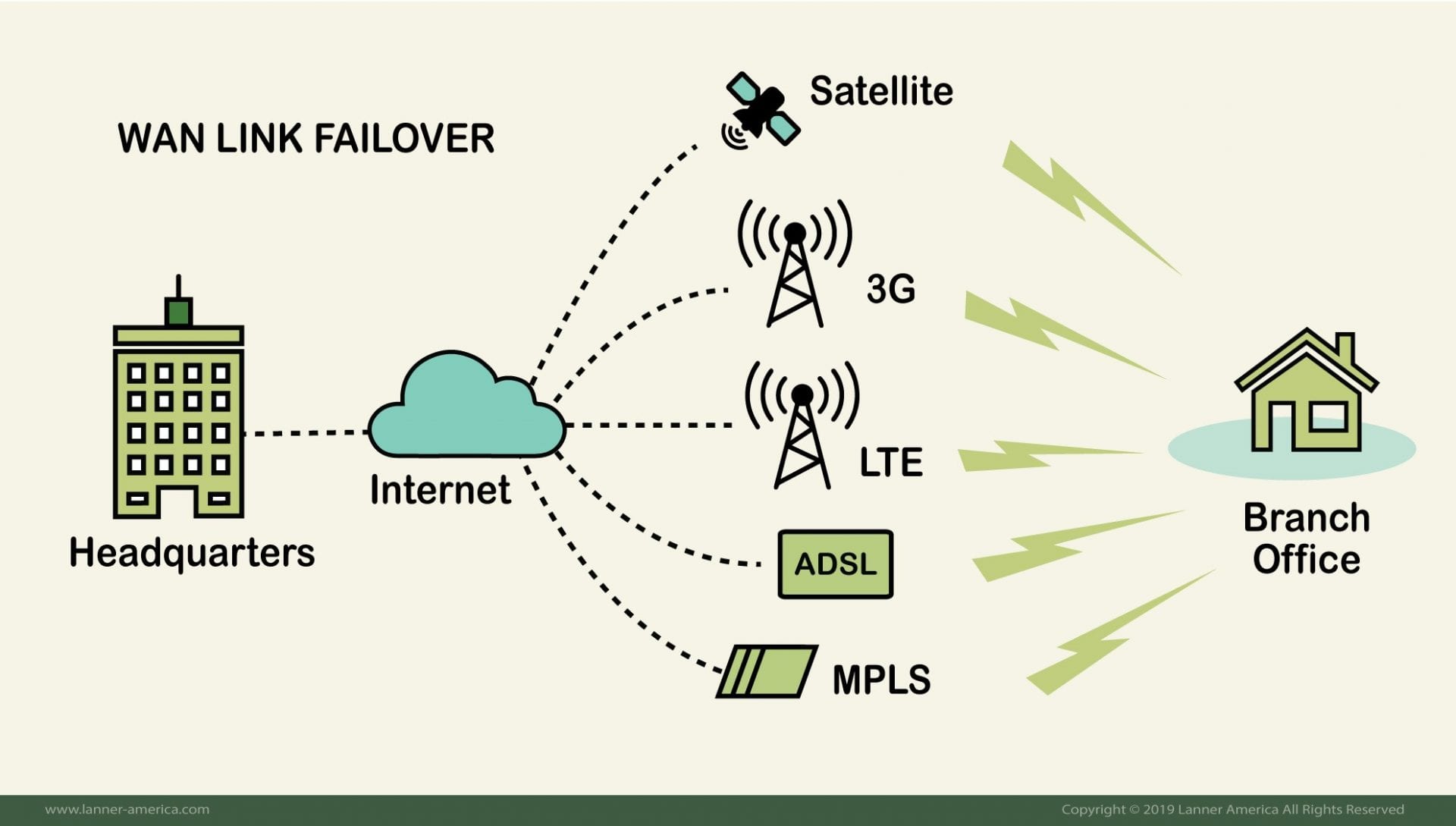
Why LTE is a Good Failover Solution?
Although having Active/Standby wired links connecting the branch office provides some redundancy, it still does not give full failover. Wired connectivity can be an excellent choice for improved speed and security, but it does not guarantee reliability. On top of that, the deployment cost can be high.
Some distributed networks also tried failover with satellite links. Although satellite provided unlimited coverage area, users soon realized that their price was very high. They were also faced with higher latency, and the satellite was not as reliable as they thought.
The best technologies to provide failover are wireless broadband.
2G and 2.5G were not entirely used as backup links because they had lower capacity and throughput. But engineers started to get interested in 3G as a failover solution. It didn’t depend on last-mile wired connectivity, and CDMA 2000 provided a “decent” bandwidth for some critical services. But this was 20 years ago.
Below is a small chart comparing latest mobile generations.
| Mobile Generation. | 2G/2.5G | 3G | 4G | LTE-A |
| Bandwidth | 14-64 kbps | 2Mbps | 250Mbps | 1Gbps |
| Technology | Digital Cellular, GPRS/EDGE/CDMA | Broad Bandwidth/ CDMA 2000 | WiMax, LTE, Unified IP. | LTE-Advanced. |
| Services | Digital Voice, SMS, high capacity, MMS | High-quality audio, video, and data | Dynamic Information access, IoT and wearable devices. | Speed boost on unlicensed bands. Can set up local networks. Public Networks like CBRS, FirstNet, and ESN |
Today, only LTE or LTE-A (Advanced) can match up for the high demand for data generated at branch offices. An LTE-A failover link can be a great backup solution to wired networks. It can support the entire Internet access, its cloud-based services and apps, and the connectivity to headquarters.
The 4G LTE Failover Solution
An LTE Failover appliance provides a secondary WAN or Internet connection over the 4G mobile broadband. This wireless link does not rely on last-mile wired connectivity, as MPLS infrastructure or fiber does. When the main wired link fails, the traffic is automatically redirected to the wireless connection, restoring network access.
How does an LTE Failover Appliance works?
The LTE failover appliance connects to the primary router and sends continuous probes to test the main WAN or Internet connectivity. Once it detects a link failure from the primary router, it takes over the main connection.
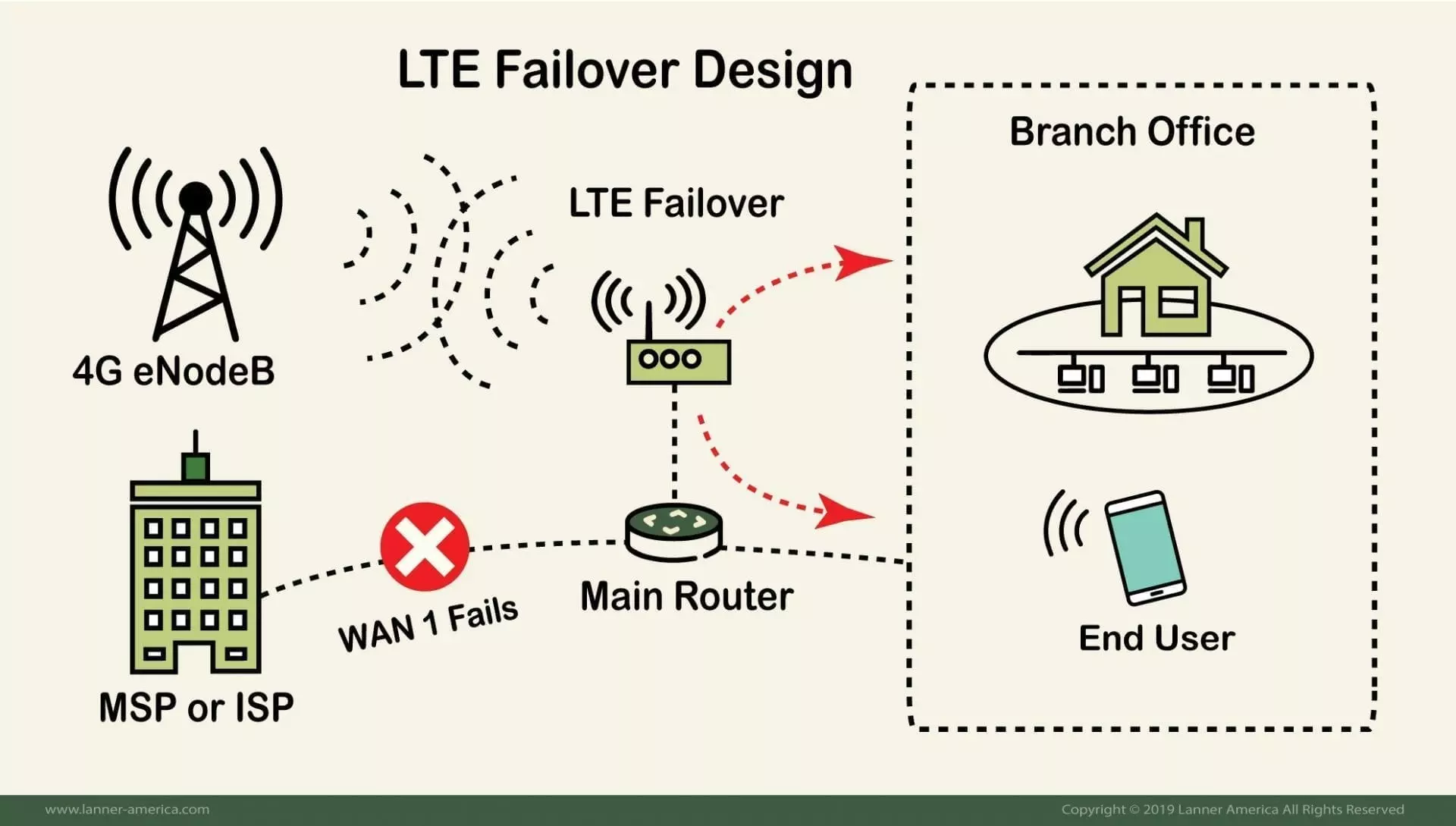
This piece of equipment connects to the primary WAN or Internet router to sense outages and is usually in standby mode. When it detects the primary connection going down, it changes to active, until the primary connection comes back up.
This appliance uses the main router as a bridge to the internal network, but it should also be capable of providing a similar internal connectivity, such as Ethernet or WiFi, in case that the entire primary router goes down.
Benefits of an LTE Failover Appliance?
- It provides LTE 4G backup on the primary WAN links.
- It provides Ethernet ports and 802.11n Wi-Fi for the internal network.
- High data throughput capacity, over 300Mbps.
- If it supports LTE-A, it can reach throughput up to 1Gbps.
The LTE Failover Module
Lanner’s PGN-300 is an 4G-LTE radio module with 2x SIM Card Readers, 2x 4G LTE Antenna, and most importantly the 4G LTE Failover for business continuity.
This module is a 4G LTE modem card compatible with Lanner Vehicle PC, Industrial PC, and Network Appliances. The PGN-300 is built-in with 4G/LTE radio modem with LTE Cat-6 embedded module. The modem card is specially designed for video surveillance and in-vehicle computing.
Opportunities for SD-WAN
SD-WAN continues to take over most of the MPLS infrastructure. It can virtualize the entire WAN while allowing full data transport. The great thing about SD-WAN is that it allows different protocols to work at the same time, from MPLS, Ethernet, 3G, and 4G.
The challenges with WAN existing infrastructure are:
- MPLS is complex and takes a long time to provision.
- Having multiple idle connections for failover can be costly.
- Inability to use 2-3 connections at the same time.
In a pre-SD-WAN environment, you might be using MPLS infrastructure as Active, the Public Internet as an Active/Backup, and the LTE as a backup network. The problem is that you might not be using the backup lines 99% of the time, but you are paying 100% of the time.
The hybrid SD-WAN architecture presents big oportunites to improve the LTE failover appliance.
The hybrid SD-WAN allows using policies to control traffic and failover. With the hybrid SD-WAN, the branch office will be re-configured more quickly and easily. Some enterprises are even using LTE as a primary link with hybrid SD-WAN only for specific applications.
An additional advantage to use LTE with SD-WAN is that as compared with MPLS, which is a circuit-based technology, 4G-LTE is packet-switched, which allows easier provisioning to a software-defined environment. What used to take months to provision a new Metro Ethernet WAN line, with SD-WAN and LTE it can take only a few minutes to provision a new link.
Summary
If your business relies on one hard-wired router with a single-point-of-failure, your entire connectivity is at risk. There is no doubt that the wired connection will fail at some point. Maybe the MSP is doing a maintenance job, a nearby construction breaks the cables or outages at near Data Centers. There are many reasons why a wired connection might fail.
But it can get more challenging in distributed networks, where multiple branch offices need reliable connectivity to the headquarters. What happens when a primary wire or router fails?
The LTE Failover appliance removes the single-point-of-failure by introducing wireless as a backup link. These appliances offer failover protection and full router redundancy, delivering business continuity to the branch.
As for today, LTE is generally considered a backup network. But soon enough it will also be used as a primary link thanks to hybrid SD-WAN technology.








